Taxonomy
Threadfin Breams, a captivating family of marine fish, are members of the Nemipteridae family, nestled within the order Perciformes. Comprising over 100 species, this family boasts a diverse range of these fish, often characterized by their distinct morphological features.
Morphology
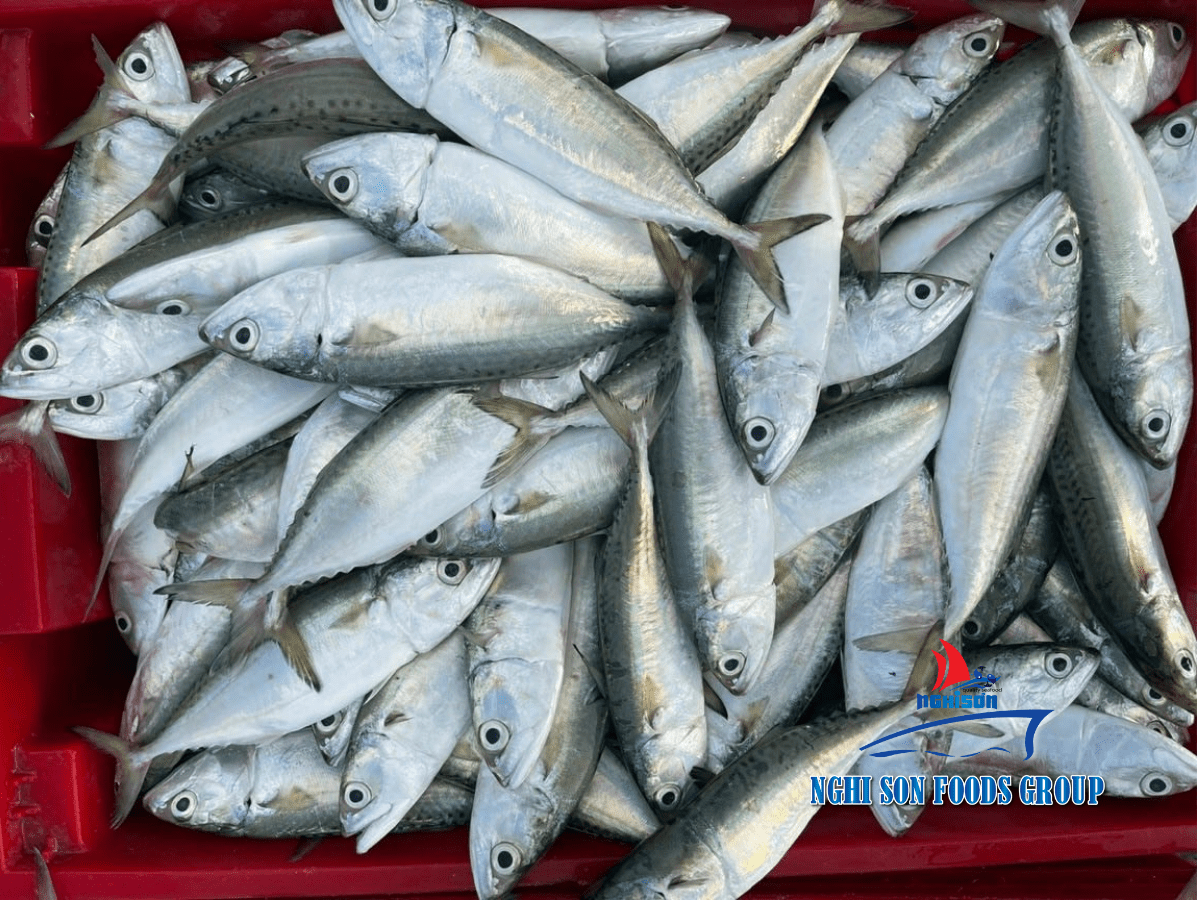
Threadfin Breams are distinguished not only by their family, Nemipteridae, but also by their intricate morphology, which has evolved to suit their varied ecological niches. Their streamlined, laterally compressed bodies facilitate quick and precise movements through the water. This design is particularly advantageous for navigating the intricate mazes of coral reefs, darting among crevices in rocky substrates, or effortlessly gliding over seagrass beds. Their fins play a crucial role in these acrobatics. Apart from the thread-like extensions on their dorsal fin spines, they boast robust pectoral fins that allow for precise control and braking during rapid maneuvers. These adaptations make them agile and efficient predators.
Their captivating dorsal fin filaments, the hallmark of Threadfin Breams, serve multiple functions. While these filaments primarily aid in predator deterrence by making them appear larger and more formidable to potential threats, they may also have roles in intraspecific communication. The colors and patterns on their bodies can vary significantly among species, contributing to their visual appeal. Shades of pink, silver, yellow, and brown intermingle in intricate patterns, often serving as camouflage in their respective habitats. Their small, cycloid scales, though unnoticeable at first glance, provide an additional layer of protection against abrasions and minor injuries, which can be common in their rocky or coral-rich environments.
The mouth of Threadfin Breams is another testament to their adaptation. Equipped with sharp, conical teeth, their mouths are perfectly suited for capturing elusive prey. This dental arrangement allows them to efficiently grasp and subdue various types of prey, from evasive crustaceans to agile small fish. The combination of morphology and feeding behavior makes them formidable hunters in their aquatic realm, allowing them to exploit a diverse range of food sources.
Habitat and Distribution
Threadfin Breams’ fascinating diversity extends to their choice of habitats and geographical distribution. Their remarkable adaptability allows them to occupy a wide spectrum of marine environments, from the bustling coral reefs of the Indo-Pacific to the more serene and sandy expanses of coastal lagoons.
Within coral reefs, Threadfin Breams often navigate intricate mazes of branching corals and rocky crevices. Here, their streamlined bodies and powerful pectoral fins come into their own, allowing them to weave effortlessly through the labyrinthine structures in search of prey and refuge from predators.
In contrast, species found in sandy or muddy substrates have developed slightly different adaptations. Their colors and patterns often match the sandy seafloor, providing effective camouflage. Additionally, their foraging strategy involves probing the substrate with their pointed snouts, revealing buried prey such as small crustaceans and worms.
Some Threadfin Bream species venture into estuarine environments, where freshwater from rivers meets the sea. These areas offer a unique mix of salinities and habitats, making them suitable for specialized adaptations in certain species. Coastal lagoons, with their mix of brackish and marine waters, are particularly attractive to these fish.
Geographically, Threadfin Breams have a sprawling range that spans from the eastern coast of Africa to the western Pacific Ocean and northern Australia. This extensive distribution showcases their ability to adapt to various environmental conditions and highlights their ecological significance in a broad range of marine ecosystems.
Reproduction and Behavior
Threadfin Breams’ reproduction and behavior offer a captivating glimpse into their life cycles and ecological roles. These fish exhibit sexual dimorphism, with distinct differences between males and females, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction typically involves the release of buoyant eggs into the water column. These eggs are fertilized externally by males releasing their sperm. This strategy increases the chances of fertilization as the eggs disperse in the water, exposing them to a greater concentration of sperm.
Upon hatching, Threadfin Bream larvae enter a pelagic phase, where they drift in the open water. During this stage, they are highly vulnerable to predation, but this phase also allows for their widespread distribution. As they mature, they undergo a remarkable transformation, adapting to the specific habitat they will inhabit as adults. This transition often involves changes in body shape, coloration, and behavior.
Some Threadfin Bream species display intricate spawning behaviors. They may form spawning aggregations, where multiple individuals gather at specific locations for mating. These aggregations can be impressive spectacles, drawing the attention of researchers and conservationists due to their ecological significance and susceptibility to overfishing.
Behaviorally, Threadfin Breams are dynamic fish. While some species are solitary hunters, others are known to form schools. Schooling behavior can serve multiple purposes, including increased protection from predators, improved foraging efficiency, and enhanced reproductive success through synchronized spawning. Their activity patterns often revolve around crepuscular periods, with peak activity at dawn and dusk when they actively hunt for food.
Territoriality is another aspect of their behavior, especially during the breeding season. Male Threadfin Breams may establish and fiercely defend spawning territories, using visual displays and aggression to deter intruders and attract potential mates.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of Threadfin Bream species spans a wide spectrum. While some species flourish and are not currently endangered, others face a multitude of conservation challenges. Factors like overfishing, habitat degradation, and ecological shifts can affect their populations. Detailed assessments and ongoing monitoring efforts are essential to craft effective conservation strategies.
Fishing and Culinary Significance
Threadfin Breams are esteemed for their culinary qualities, boasting tender and flavorful flesh. In numerous coastal communities, they form a dietary staple and bolster the livelihoods of artisanal fishermen. The sustainability of fishing practices is critical to ensure both the health of these fish populations and the well-being of fishing communities.
Aquarium Care and Challenges
Keeping Threadfin Breams in home aquariums presents a unique set of challenges. These fish have specific habitat requirements and can exhibit territorial behavior. To provide proper care, aquarists must ensure suitable tank conditions, including tank size, water parameters, and adequate hiding places. Compatibility with other fish species should be diligently considered to prevent aggression.
Scientific Research and Conservation Efforts
Scientific inquiry into Threadfin Breams encompasses an array of topics, including behavior, ecology, genetics, and taxonomy. Conservation endeavors may entail the establishment of marine protected areas (MPAs) and the promotion of sustainable fishing practices to safeguard populations and their habitats.
Legal Regulations and International Trade
The international trade of Threadfin Breams is subject to stringent regulations overseen by organizations such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). Furthermore, national and regional fisheries management organizations institute regulations to ensure the sustainable harvest of these fish species, preserving both their ecological roles and their significance in human cuisine.
Intricately woven into the rich tapestry of marine life, Threadfin Breams continue to captivate researchers, conservationists, and seafood connoisseurs alike.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.